Project Scope |
|
| Project Leads | |
| Chris Wells, Roche | chris.wells.cw1@roche.com |
| Mireille Lovejoy, GE Healthcare | Mireille.lovejoy@gehealthcare.com |
| Alex Pearce, PHUSE Project Assistant |
|
|---|
|
| Objectives & Deliverables | Timelines |
| Release of draft White Paper | Q3 2022 |
| Publish White Paper | Q3 2023 |
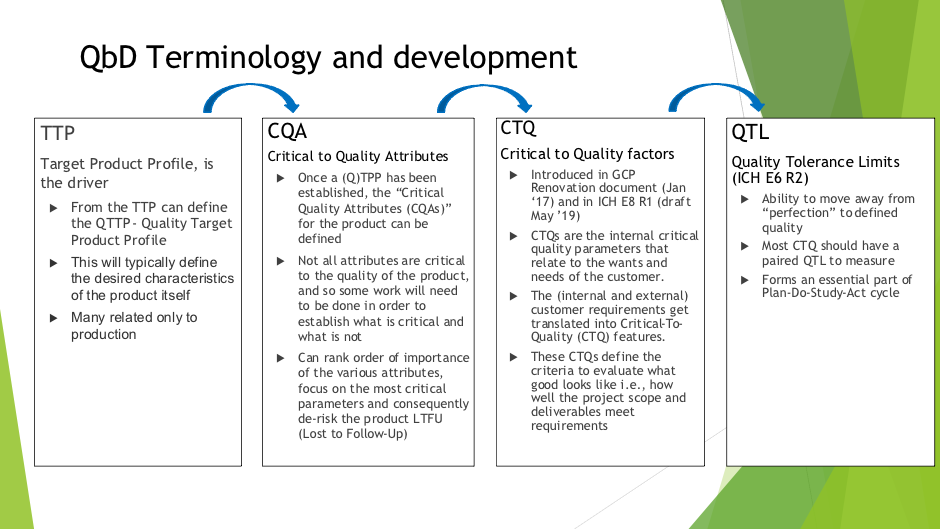
Problem Statement QTLs - the role they play in defining quality within the QbD framework, their relationship to Critical to Quality factors, associated methodologies and the interpretation of them have not been fully defined in clinical development, in particular where early development/small studies, bio equivalence studies and complex designs are concerned. Problem Impact This will impact the whole clinical development process and allow the move away from perfection to a defined and achievable quality, from which continuous quality improvement can begin. |
| Terminology Example:
|